Data Transmission is the process of sending and receiving data via
cables (e.g., telephone lines or fibre optics)
or wireless relay systems. Because ordinary telephone circuits pass signals
that fall within the frequency range of voice communication (about 300–3,500 hertz), the high
frequencies associated with data transmission suffer a loss of amplitude and
transmission speed. Data signals must therefore be translated into a format
compatible with the signals used in telephone lines. Digital computers use a modem to transform outgoing digital electronic
data; a similar system at the receiving end translates the incoming signal back
to the original electronic data. Specialized data-transmission links carry
signals at frequencies higher than those used by the public telephone network.
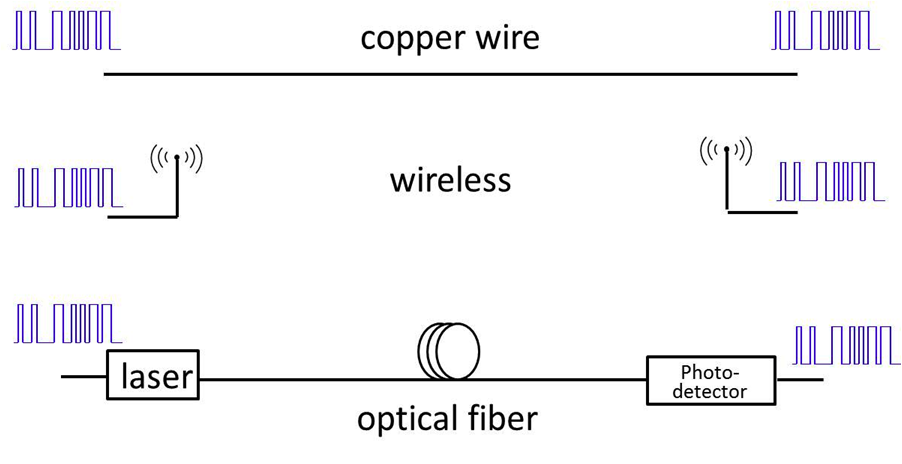 |
| Data travels in many types; either though copper wires, wireless connection, or though optical fiber. |
The
physical transfer of data over communication channel or medium such as copper
wires, optical fibers, wireless channel and storage devices. Data are represented as electromagnetic
signals such as an electrical voltage, radio wave, microwave or infrared
signal.
No comments:
Post a Comment